Pricing in marketing is a process by which businesses decide on a specific price for their products and services. The price for products and services takes into account many different factors in order to accurately reflect accurate market value. Pricing is an extremely integral part of marketing.
In this article we will take a look at different types of pricing strategies in marketing. We will discuss what makes them unique and how you can use these strategies to accurately price your products or services in the marketplace.
Pricing Strategy Defined
Before we dive into the different types of pricing strategies in marketing it’s important to define what a pricing strategy is and what it consists of. A pricing strategy in marketing is a system or model that is used to establish price for products and services.
Recommended Reading: Strategies for Market Penetration to Increase Sales and Grow Your Online Business
It is meant to help businesses establish prices that will fit the operational efficiency for their niche while taking into account competition and customer demand. Pricing strategy takes into account some of the following business factors:
- Target profit margin
- Revenue goals
- Target audience
- Product or service competition
- Product life-cycle
- Economic trends
The ideal pricing strategy is meant to not only maximize your revenue but also provide value for your customers.
Penetration Pricing

Penetration pricing is a pricing strategy that is used by businesses to attract customers to a new product or service. This is done by offering the product or service at a very low price during its initial launch.
Offering a lower price for a temporary period of time allows new products and services to “penetrate” the market and take away customers from their competitors. This strategy relies heavily on low prices in order to attract a wide base of customers and then slowly increase the prices on them over time.
Examples of Penetration Pricing
An example of penetration pricing includes The Wall Street Journal. You initially sign up at a very low rate and later they will increase the price on you.

Economy Pricing

Economy pricing is a pricing strategy in which a low price is given to a product or service due to decreased costs. The price improvement in production, marketing and or operations is passed onto the customer.
Economy pricing is a volume-focused pricing strategy which focuses on pricing goods low and making small profits on massive volume. This kind of pricing strategy tends to be used for everyday essential items such as:
- Generic groceries
- Medication
- Commodity goods
- Generic clothing (socks, underwear)
Economy pricing benefits companies who tend to have lower overhead costs and have the ability to sell large volumes in order to generate profits.
Example of Economy Pricing
A common use of economy pricing in marketing includes supermarket store brands such as Meijer, Kroger, WallMart, Aldi and others. They all have versions of their popular brands but at much lower prices than those of other well known brands.
Premium Pricing

In a premium pricing strategy businesses and brands price their products very high in order to present a luxury or premium image of their brand and products.
It is also commonly referred to as prestige pricing and has a central focus on presenting a high perceived value for its products and services. It gives brands an exclusivity feel due to higher than normal prices, which tends to be associated with luxury brands.
This type of pricing strategy is meant to represent a status and as a result prices tend to be much higher in a premium pricing strategy. Premium pricing tends to be most commonly seen in fashion, sports automobiles, private flights and more.
Example of Premium Pricing

Tom Ford is a high end fashion brand that has extremely high prices for its suite of unique fashion products. The brand is constantly worn by A-list celebrities, athletes and people who have the money to spend $2,200 on a pair of boots.
Price Skimming

Price skimming is an interesting pricing strategy in which brands and companies charge a very high price for new products and services when they initially come out and then slowly lower the price as demand begins to fall.
The key with price skimming is the fact that prices are lower gradually over time, not immediately. A main reason that price skimming is used in marketing is to help companies recoup their sunk costs and sell products at higher margins for a temporary period of time.
Price skimming doesn’t work for a long period of time due to the fact that it impacts the customer experience in a negative way.
Example of Price Skimming
A perfect example of price skimming is new technology products. This can include:
- Televisions
- Gaming systems
- Video games
- Cell phones
- Laptops
- Desktops
The price of new technology products is initially very high and gets slowly decreased over time as products become outdated over time.
Psychological Pricing

As the name implies, psychological pricing targets the human psyche through neuromarketing techniques in order to induce the purchases of products or services. Psychological pricing is a methodology for pricing products in a way that makes them more attractive to consumers.
Recommended Reading: Psychographic Segmentation in Marketing
This can include deals that cause FOMO for the customer and makes it hard for them to resist a good deal.
Example of Psychological Pricing
A very common and obvious example of psychological pricing includes pricing a $100 product or service at $99.99. Believe it or not, but your brain is likely to consider purchasing an item that flat out says $100, compared to a product that is priced at $99.99.
Even though the difference is a measly penny, the psychological pricing is in place to help induce you to think that it’s a fair price.
Another example is the BUY ONE GET ONE FREE deal option. Although the cost of the second item is already baked into the original price, this psychological pricing trick causes you to perceive this kind of pricing as a deal.
Bundle Pricing

The bundle pricing strategy is a great marketing pricing strategy that is effective in helping increase the average order value . The bundle pricing strategy is when you offer customers two or more related items that are meant to compliment their original purchase. It’s a cross selling technique that can bring a ton of value to both businesses and customers.
For the bundle pricing strategy to be effective it’s important to recommended additional items to your customers that will complement their main purchase.
Example of Bundle Pricing

Amazon is notorious for offering their customers similar or related products through their frequently purchased together option. This helps induce customers to add additional products to their carts that are related to their main purchase.
We also offer our Growth Hacking Suite in a Bundle Pricing
Geographical Pricing

In order to use the geographical pricing strategy it’s very important that you have a clear understanding of the different markets. It’s a pricing strategy in which products and services are priced differently depending on the different geographical locations of a business.
It can be an effective way to make your margins a bit more stable. Pricing certain items higher in a different location can help you capture a higher margin and smooth out your profitability.
Example of Geographical Pricing
A good example of geographical pricing is the cost of gas in one area of the city, vs the cost of gas in another area of your city. You might see gas prices lower in an area of the city which has less disposable income versus higher gas prices in an area with more disposable income.
Captive Pricing

Captive pricing is a pricing strategy that is used when a core product has multiple accessory products that can be purchased alongside it. This type of pricing strategy is most often utilized with core products that will be used and will need additional restocking products in order to function.
The two main components which involve the captive pricing model is having a core product and a captive product.
Example of Captive Pricing
A great example of the captive pricing model is a coffee maker and coffee pods.
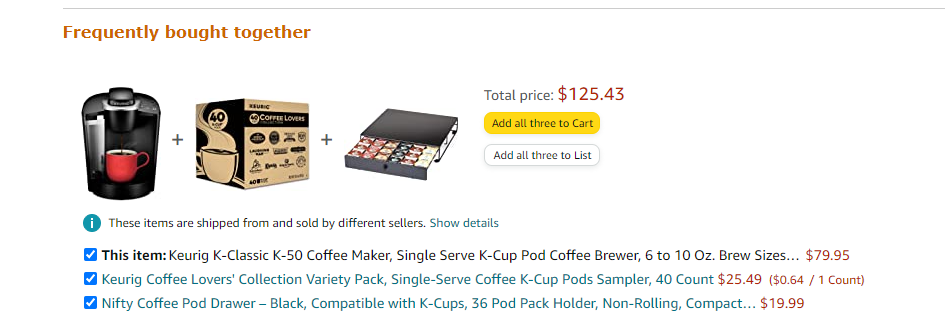
The coffee maker in this case is the core product and the coffee pods function as the “captive product”. Captive products tend to be repurchased over and over again because they get consumed or used up.
Dynamic Pricing

Dynamic pricing is a pricing strategy which is constantly adjusted based on current market and consumer demand. It is also commonly referred to as demand pricing, surge pricing or time based pricing.
Dynamic pricing is typically used in order to stay competitive, keep healthy profit margins and to satisfy demand.
Example of Dynamic Pricing
One of the most common uses of the dynamic pricing model is used by hotels. Pricing is decided by algorithms based on current demand, competitor pricing and much more. A few other businesses use the dynamic pricing model include:
- Taxi services – (Uber and Lift)
- Airlines
- Event venues
- Stock prices
Conclusion
Knowing different marketing pricing strategies that exist can leave you a bit overwhelmed on the best way to price your products or services. Before you make a decision on what kind of pricing strategy to use it’s important to first define your business type. Define how it functions and operates and what kinds of products and services it offers. Once you fully define these parts, picking the right pricing strategy for your business becomes much easier.